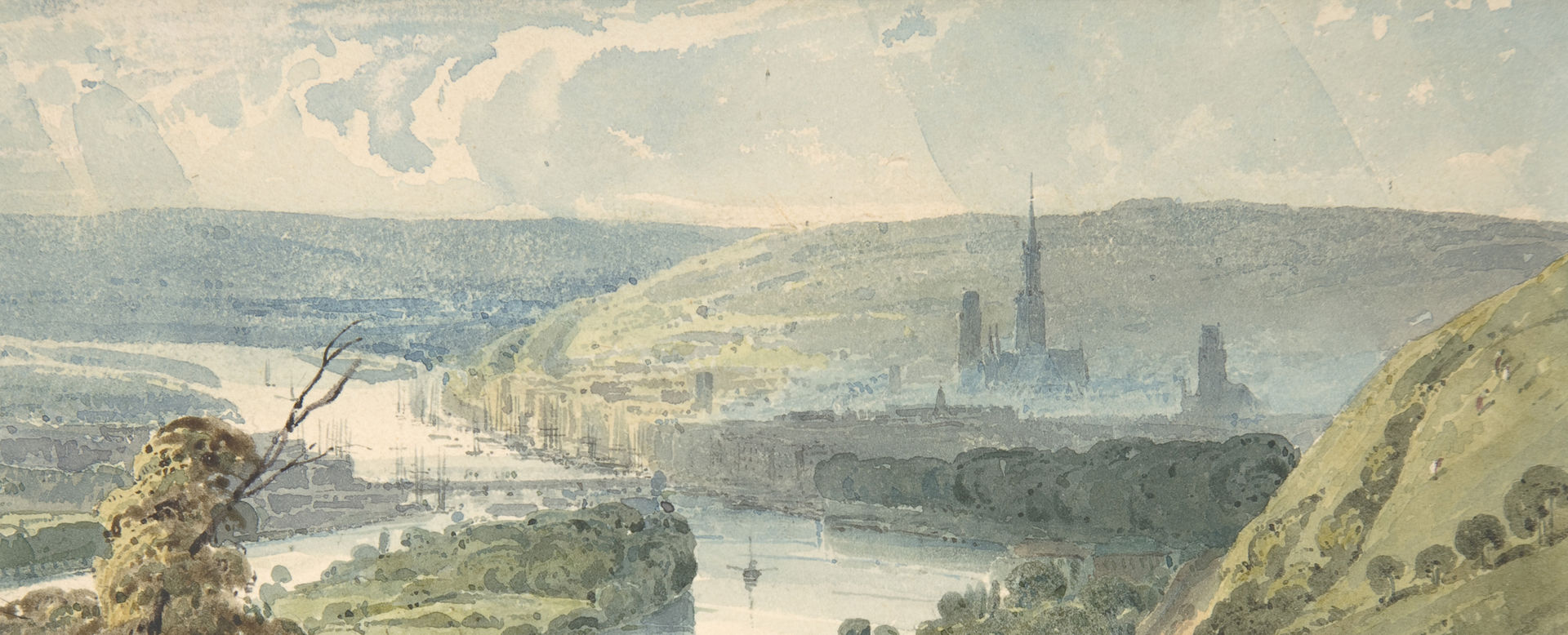Design for a Gold and Red-Gold Earring with Turquoises and Black Pearls
Anonymous, French, 19th century French
Not on view
Drawing with a design for a gold earring with turquoises and black pearls that is part of a collection of 85 drawings with figurative designs for earrings, brooches, pendants and other jewels, possibly real-sized, created with graphite and gouache and heightened with gold inside lithograph frames. These designs are all characteristic of the period between 1870 and 1900, when jewelry design saw a great degree of innovation and creativity in both style and technique. Some of the most important innovations that took place at this time included the setting of diamonds without metal on the back to reinforce the refraction of light on the cut surfaces of the stones, and the use of gold granules and cannetille (scrolls of metal strips) in the creation of fine metal surfaces. (Semi-)precious stones continued to be used in jewelry design at this time, especially with the discovery of diamond mines in South Africa, although alternative techniques, many of them inspired on ancient jewelry, were also common: Enamel in its different application techniques (including champlevé, cloisonné, and low-relief) was particularly popular. In addition to enamel, colored glass was used to add touches of color to the metallic structures that formed the base of the jewels. In general, jewelry design during this period became more complex, and the colors in nature were mimicked by the color of gemstones used for jewelry design: the designs were elaborate and relied in the natural beauty of cabochon gems, curving, and figurative designs with symbolic meaning, typical of the Arts and Crafts movement. Towards the end of the nineteenth century, the Art Nouveau movement created sinuous and organic pieces that moved away from conventional stones and put emphasis on the subtle effects of materials such as glass, horn and enamel. The European Middle Ages and the Renaissance, as well as civilizations of the Mediterranean, and even Japan, became important sources of inspiration for jewelry design at this time.
This design for a gold earring is made up of four trapezoid-shaped gold frames held together by red-gold cylinders with thin engraved stripes and a vertical strip of square-cut turquoises. From the bottom edge of the lower trapezoid frame hang five teardrop-shaped black pearls, each attached to the frame by a small gold granule. Turquoises were particularly important design elements at the time of creation of this design because of their association with Maghreb and other African-Mediterranean civilizations that provided sources of inspiration at the time. The stones could have been replaced by blue enamel or blue-colored glass stones in the manufacture of the jewel, both techniques widely used at the time. The drawing lies over a black gouache background inside a cream lithograph frame.