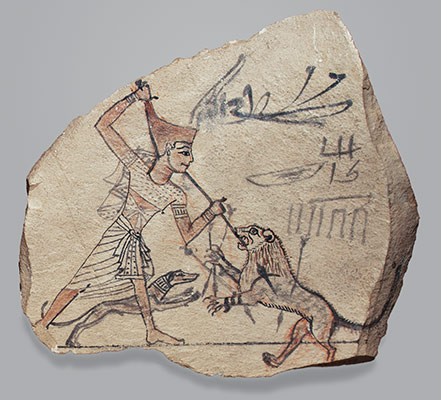
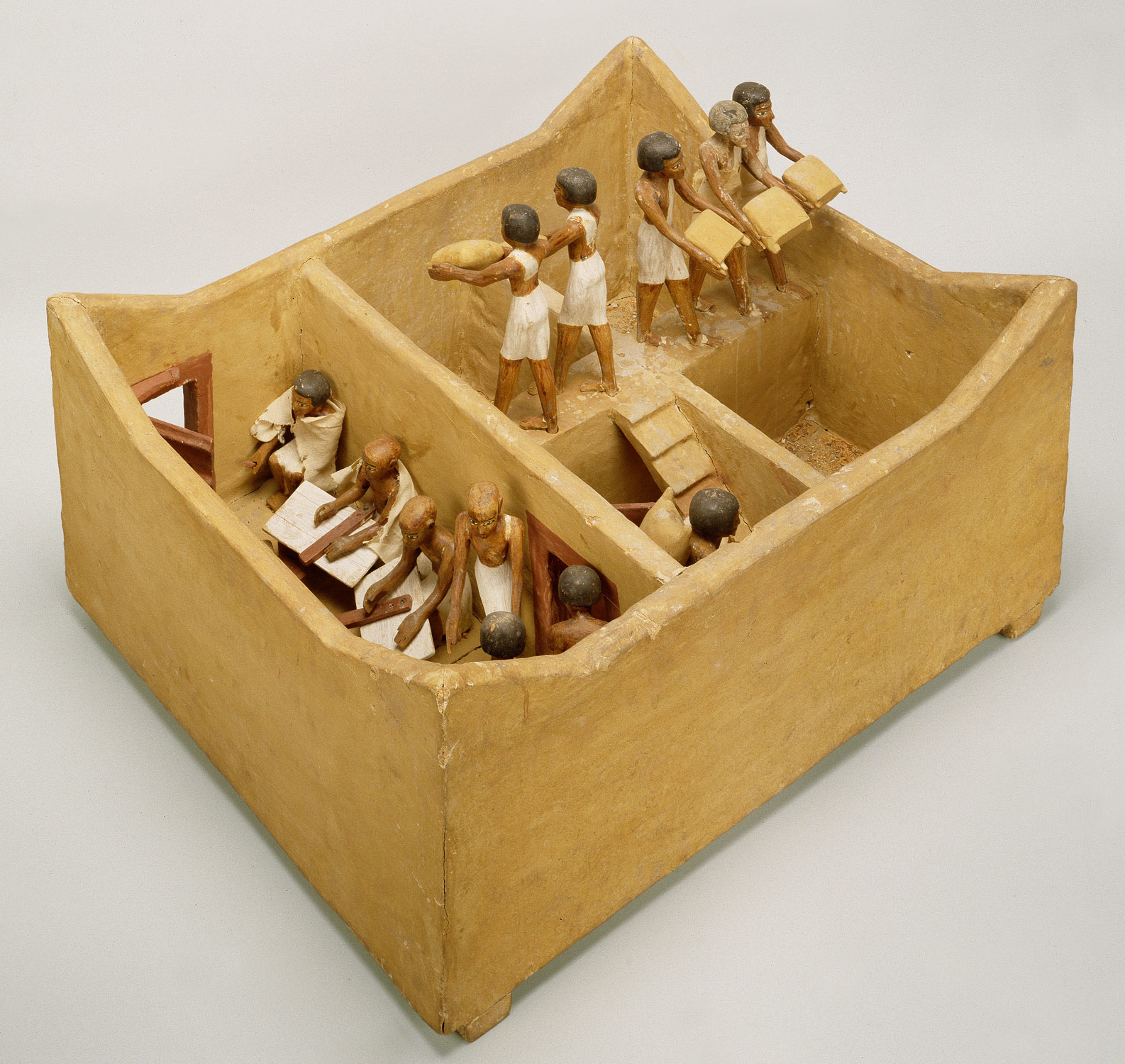
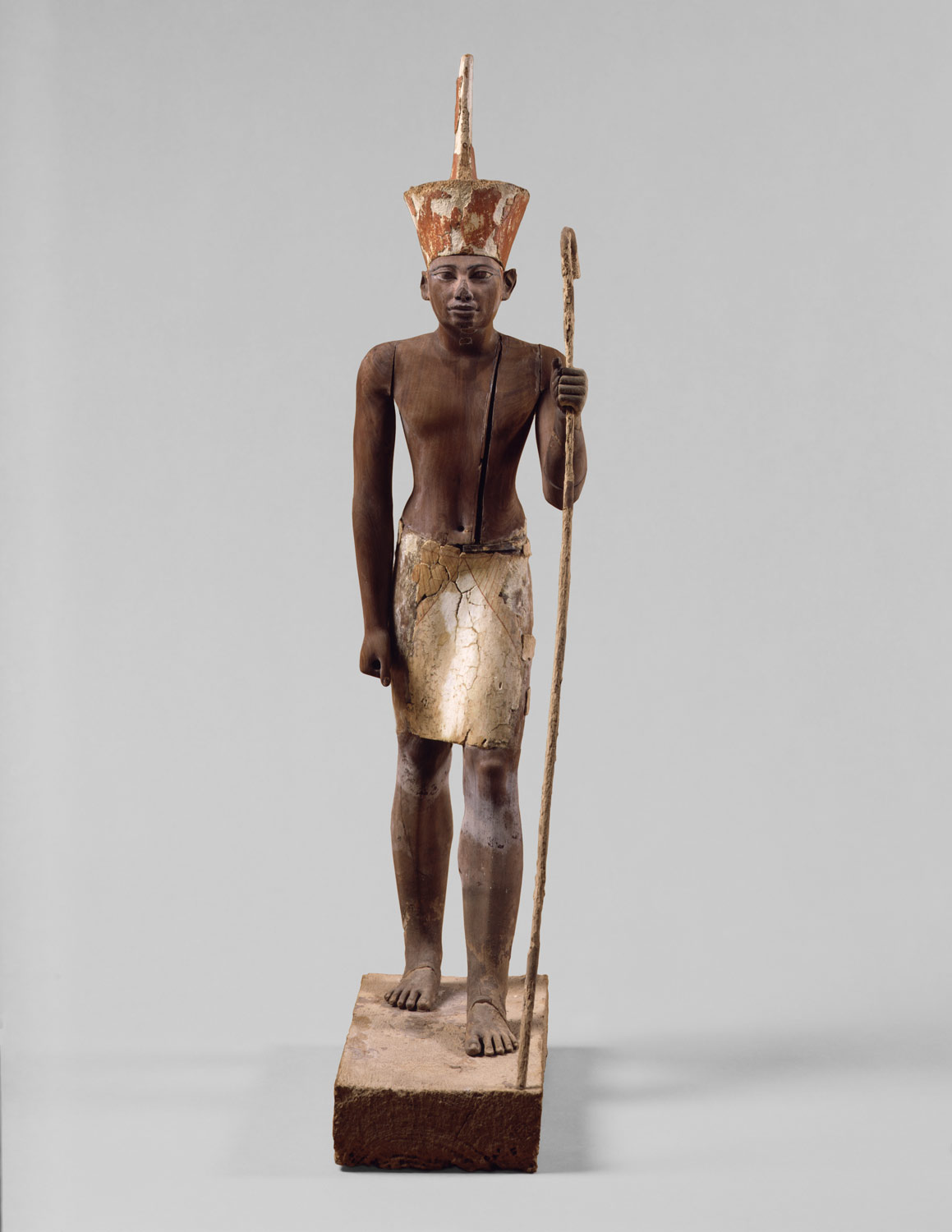
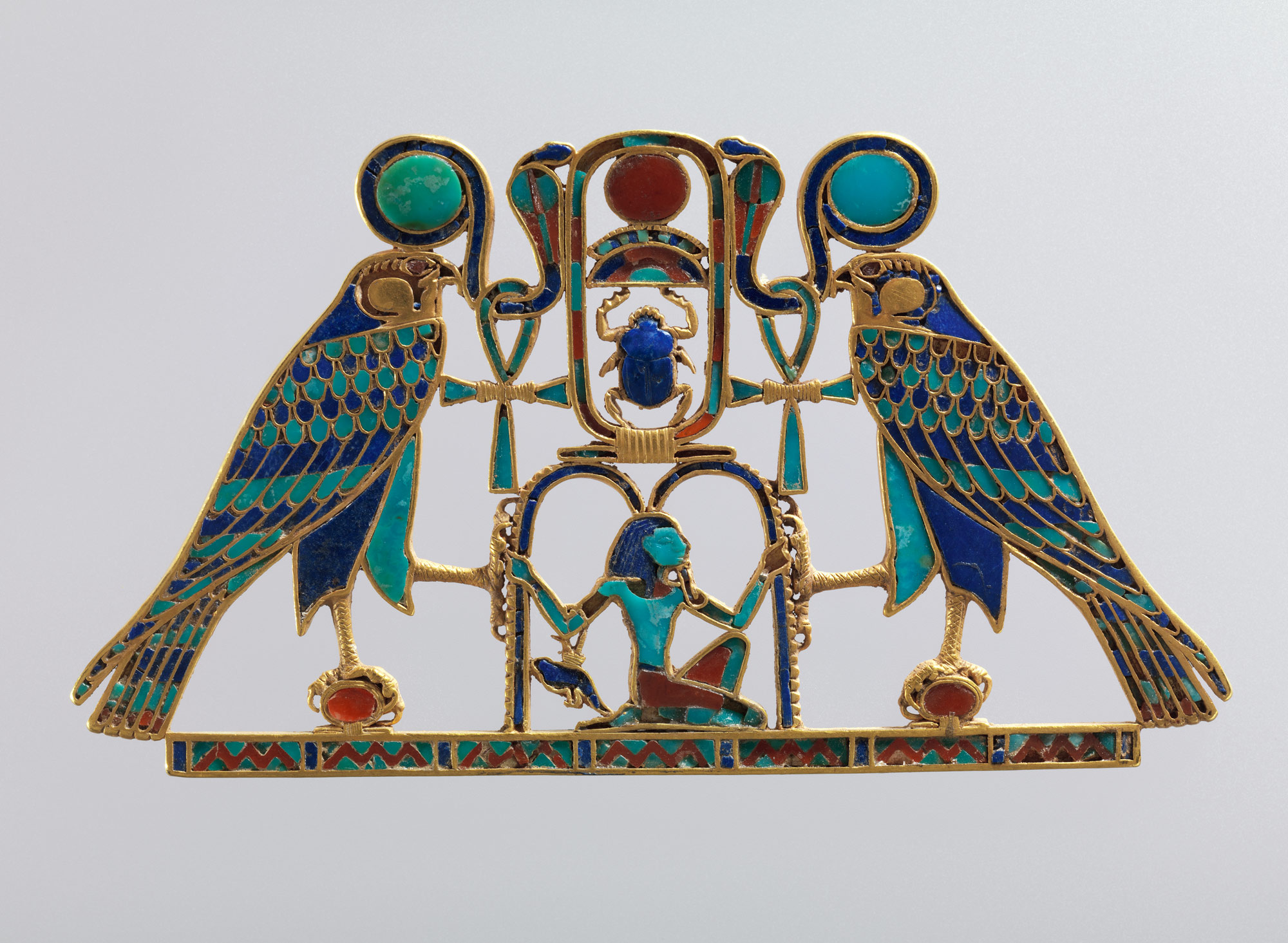
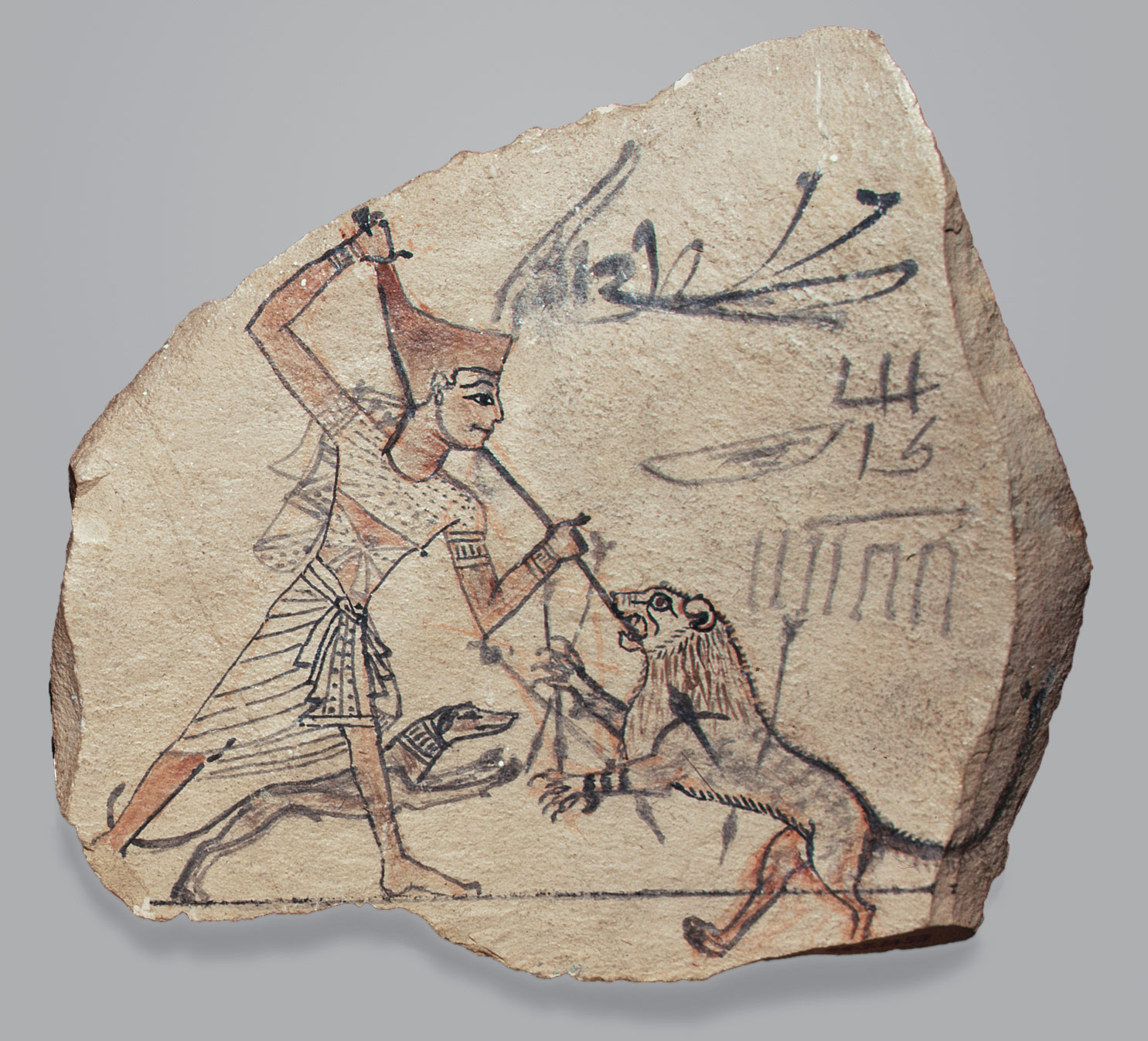
Upper and Lower Egypt are reunited by Theban king Nebhepetre Mentuhotep II who establishes the capital at Thebes, then Itj-tawy. Egypt is briefly ruled by competing dynasties from western Asia and its environs. Reunification occurs again under Ahmose I and a time of economic and artistic prosperity ensues. Hatshepsut, the most powerful female ruler of pharaonic history, builds her unique funerary temple in western Thebes. After the reign of Ramesses III, Egypt’s power gradually declines, leading to the Third Intermediate Period.
Egypt, 2000–1000 B.C.
Timeline
2000 B.C.
1750 B.C.
ANCIENT EGYPT
ANCIENT NUBIA (ALSO SEE SUDAN)
1750 B.C.
1500 B.C.
ANCIENT EGYPT
ANCIENT NUBIA (ALSO SEE SUDAN)
1500 B.C.
1250 B.C.
ANCIENT EGYPT
ANCIENT NUBIA (ALSO SEE SUDAN)
1250 B.C.
1000 B.C.
ANCIENT EGYPT
ANCIENT NUBIA (ALSO SEE SUDAN)
Overview
Key Events
-
ca. 2030–1640 B.C.
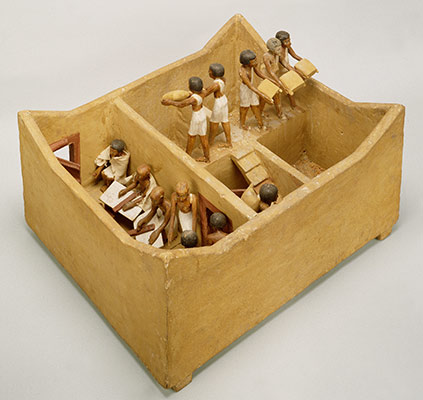
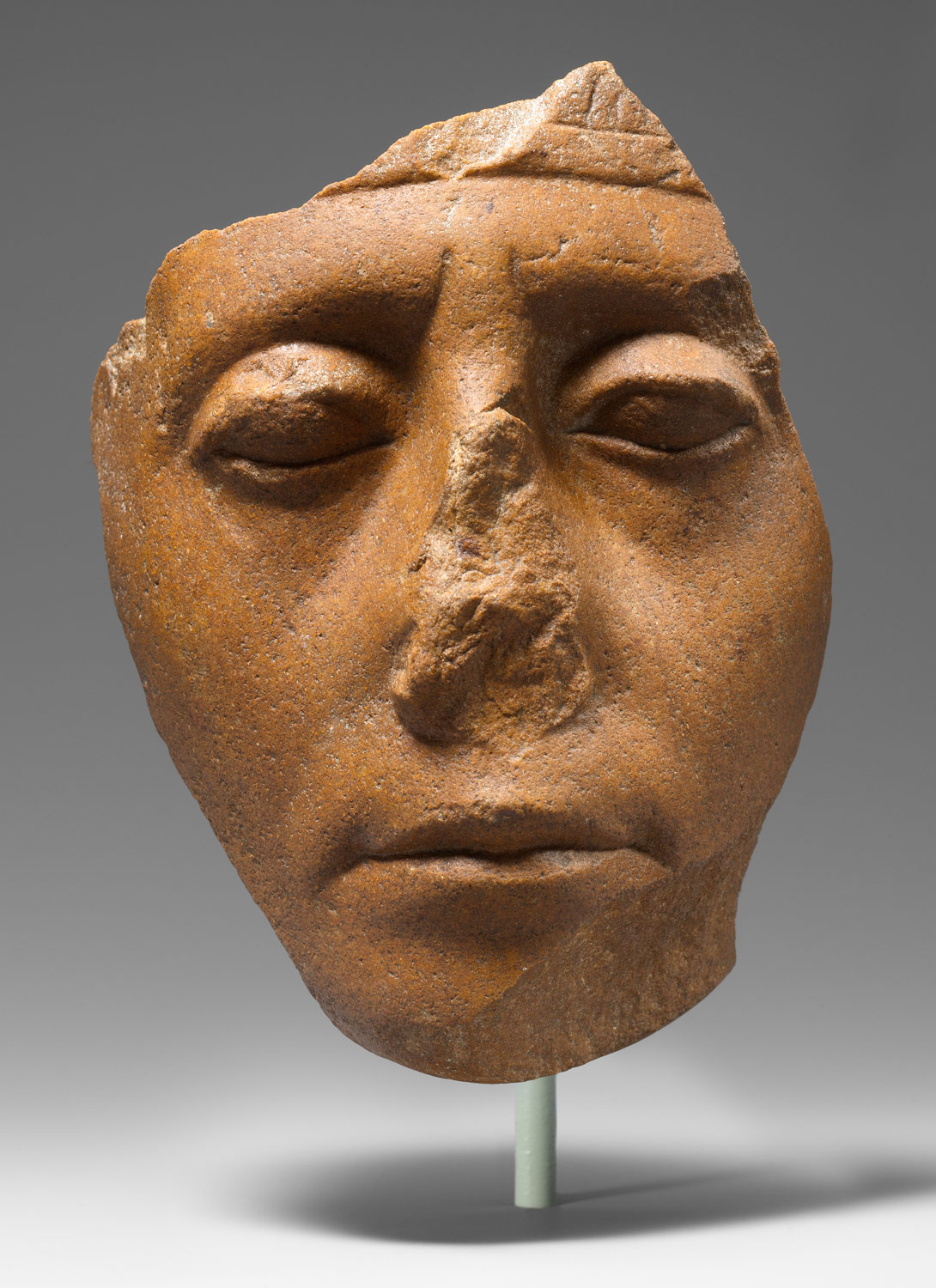
(Middle Kingdom, mid-Dynasty 11–Dynasty 13) The Theban king Nebhepetre Mentuhotep II reunites Upper and Lower Egypt, establishing the capital at Thebes and ushering in the Middle Kingdom. A renewed flowering of the arts is evident, especially in Mentuhotep’s innovative funerary temple in western Thebes, and in the exquisite painted reliefs decorating this structure and the tombs of officials in the surrounding cemeteries.
-
ca. 1981–1802 B.C.
(Dynasty 12) Amenemhat I, founder of Dynasty 12, moves the capital from Thebes to Itj-tawy in the north. The architecture and sculpture of this dynasty show clear links with the artistic traditions of the late Old Kingdom, while creating powerful and distinctive new artistic forms. Egyptians trade extensively with cultures of the eastern Mediterranean and control Lower Nubia, building a series of forts on either side of the second cataract of the Nile.
-
ca. 1640–1550 B.C.
(Second Intermediate Period, Dynasties 15–16 in Lower Egypt, Dynasty 17 in Upper Egypt) During the Second Intermediate Period, Egypt is ruled once again by competing dynasties. The north is controlled by the Hyksos, descendants of people from western Asia who had settled in the eastern Nile Delta. The Hyksos form an alliance with the rulers of Kerma in Nubia against the Egyptian dynasty based in Thebes.
-
ca. 1550–1070 B.C.
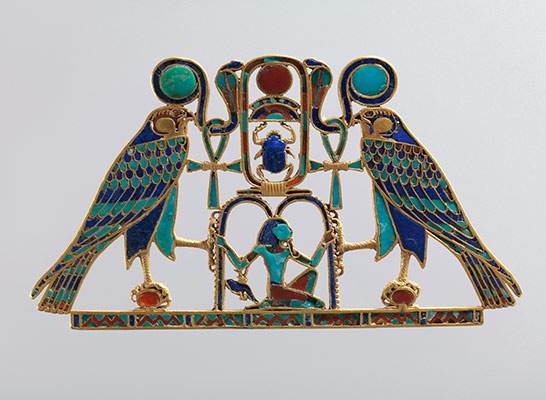
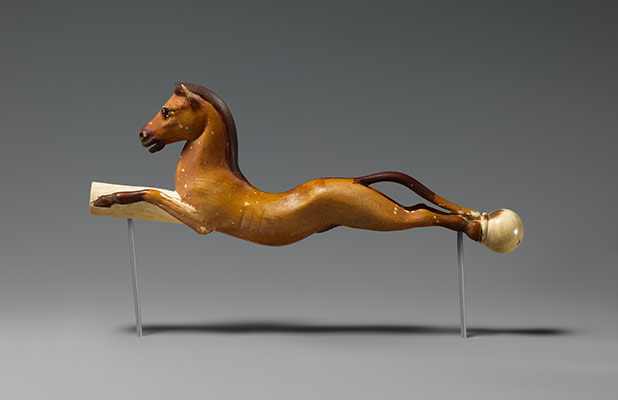
(New Kingdom, Dynasties 18–20) The Theban king Ahmose I reunites Egypt, founding Dynasty 18. A series of great warrior kings, in particular Thutmose III, extend Egyptian influence in western Asia throughout the Levant to the borders of the Hittite empire. Egypt also gains control of Nubia as far south as the fourth cataract. Through military campaigns, trade, diplomatic gifts, and tribute, Egypt attains a level of wealth previously unknown. This wealth is a catalyst for the third great flowering of Egyptian culture, marked by royal building campaigns unequaled since the time of the pyramids. The period also produces an abundance of nonroyal art, including statuary, relief, painting, and all types of minor arts.
-
ca. 1550–1295 B.C.
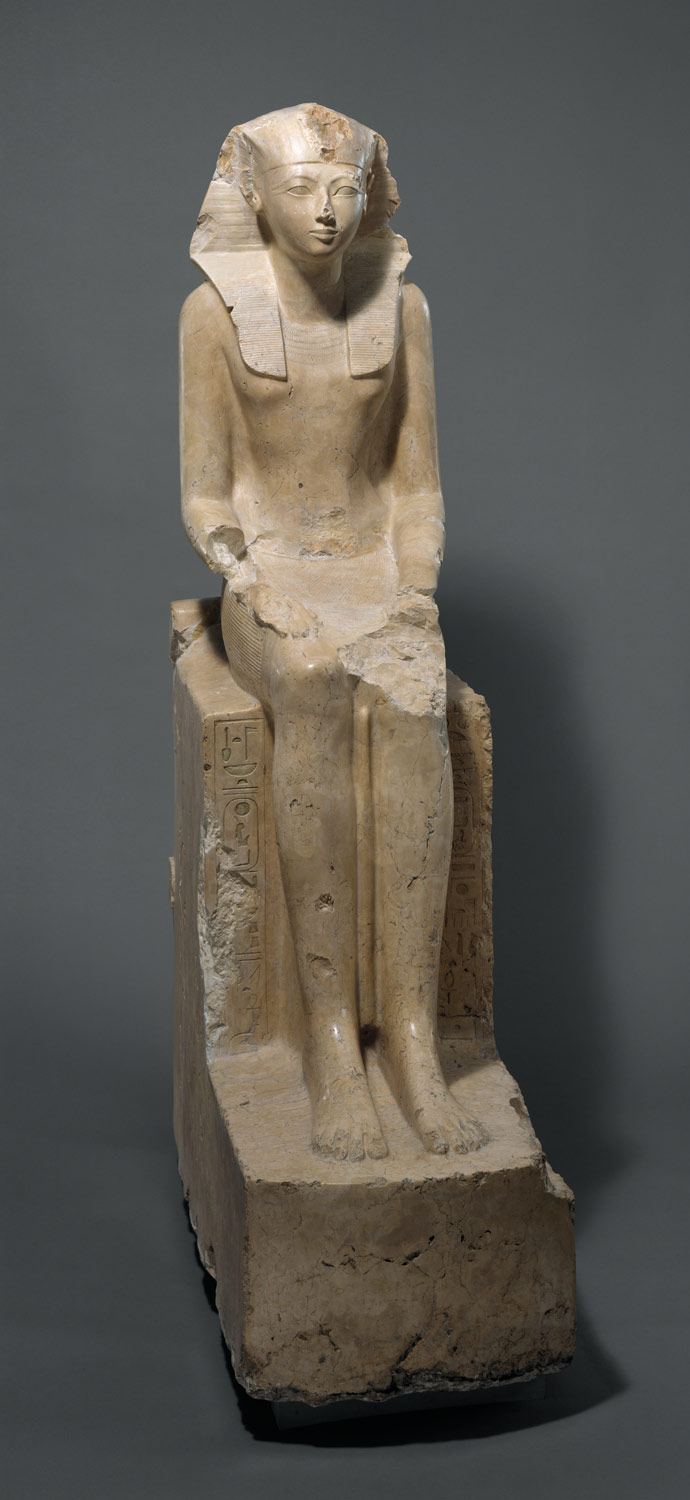
(Dynasty 18) Although Memphis is the chief administrative center, Thebes, cult center of the god Amun-Re and home of the dynasty, remains important as a religious and cultural center. Influenced by the temple of Mentuhotep II, Hatshepsut, the most powerful female ruler of pharaonic history, builds her unique funerary temple in western Thebes. Akhenaten, ruling near the end of the dynasty, breaks with tradition by establishing the first monotheistic religion. Although the new religion ends with his death, the influence of artistic innovations introduced during Akhenaten’s reign continues into the next dynasty.
-
ca. 1295–1070 B.C.
(Dynasties 19–20, Ramesside Period) Dynasty 19 is founded by Ramesses I, a high military official from the eastern Delta. Ramesses II, most famous of the Ramesside kings, reasserts Egypt’s hegemony over the Levant in the east and Nubia to the south. The Ramesside Period is best known for its monumental structures—the temple of Osiris built by Seti I at Abydos; the great hypostyle hall in the temple of Amun-Re at Karnak; the rock-cut temple of Ramesses II at Abu Simbel in Lower Nubia; and Medinet Habu, the mortuary temple of Ramesses III in western Thebes. After the reign of Ramesses III, Egypt’s power gradually declines, leading to the Third Intermediate Period.
-
ca. 1070–712 B.C.
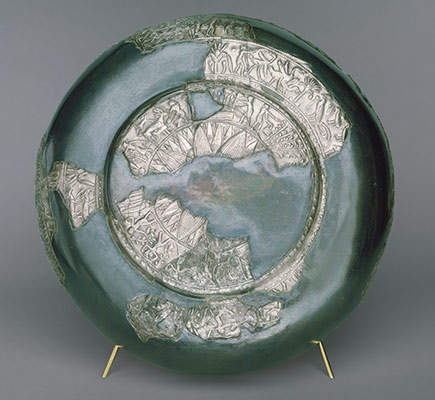
(Third Intermediate Period, Dynasties 21–24) This period is a time of competing dynasties and of gradual fragmentation into yet smaller political units.
Citation
“Egypt, 2000–1000 B.C.” In Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History. New York: The Metropolitan Museum of Art, 2000–. http://www.metmuseum.org/toah/ht/?period=03®ion=afe (October 2000)
Related
Map