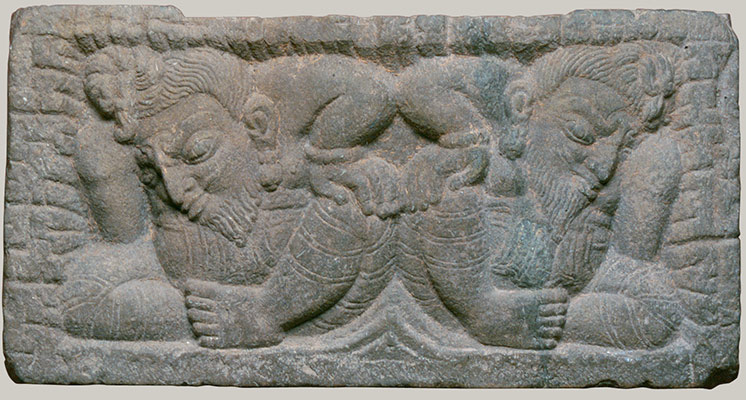
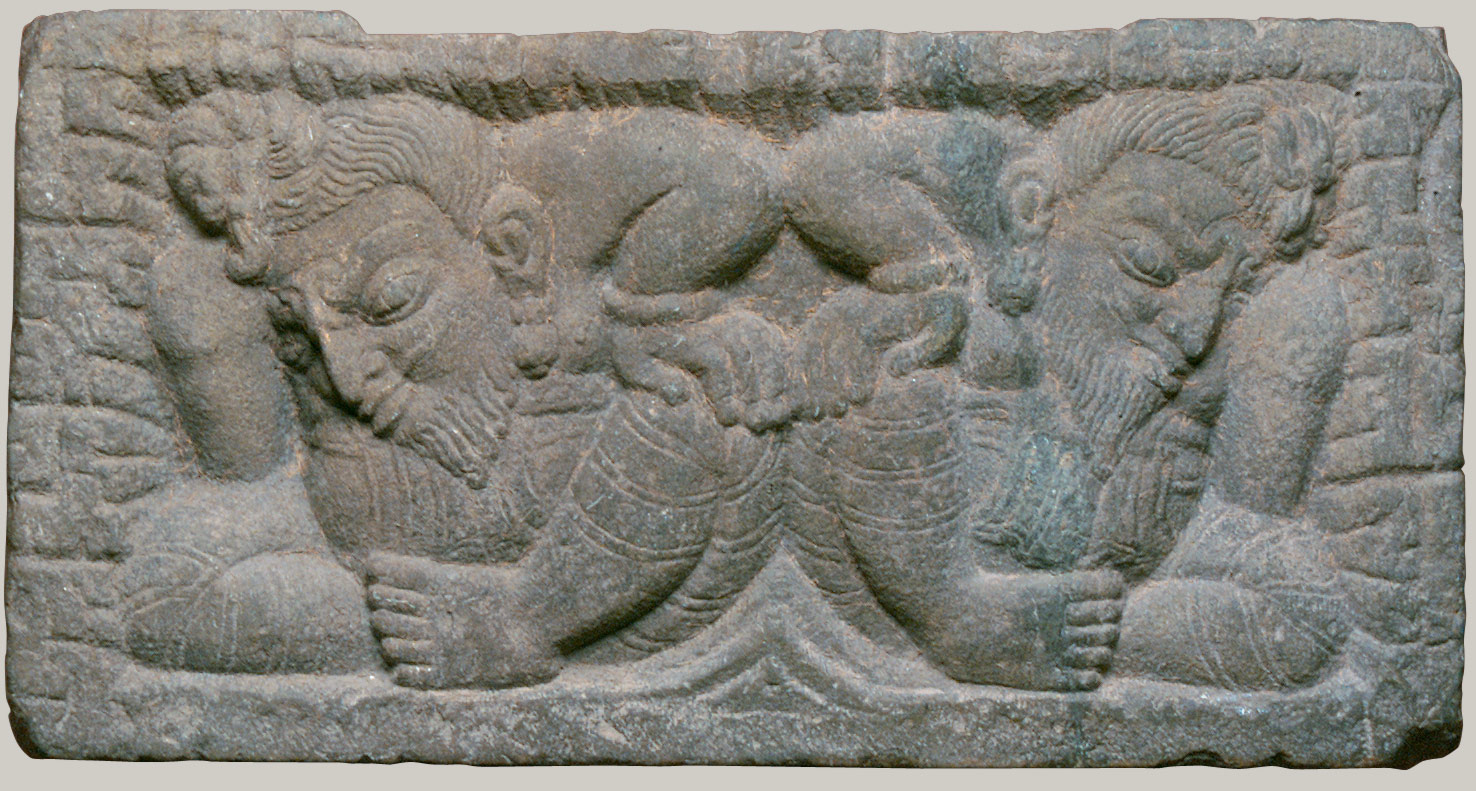
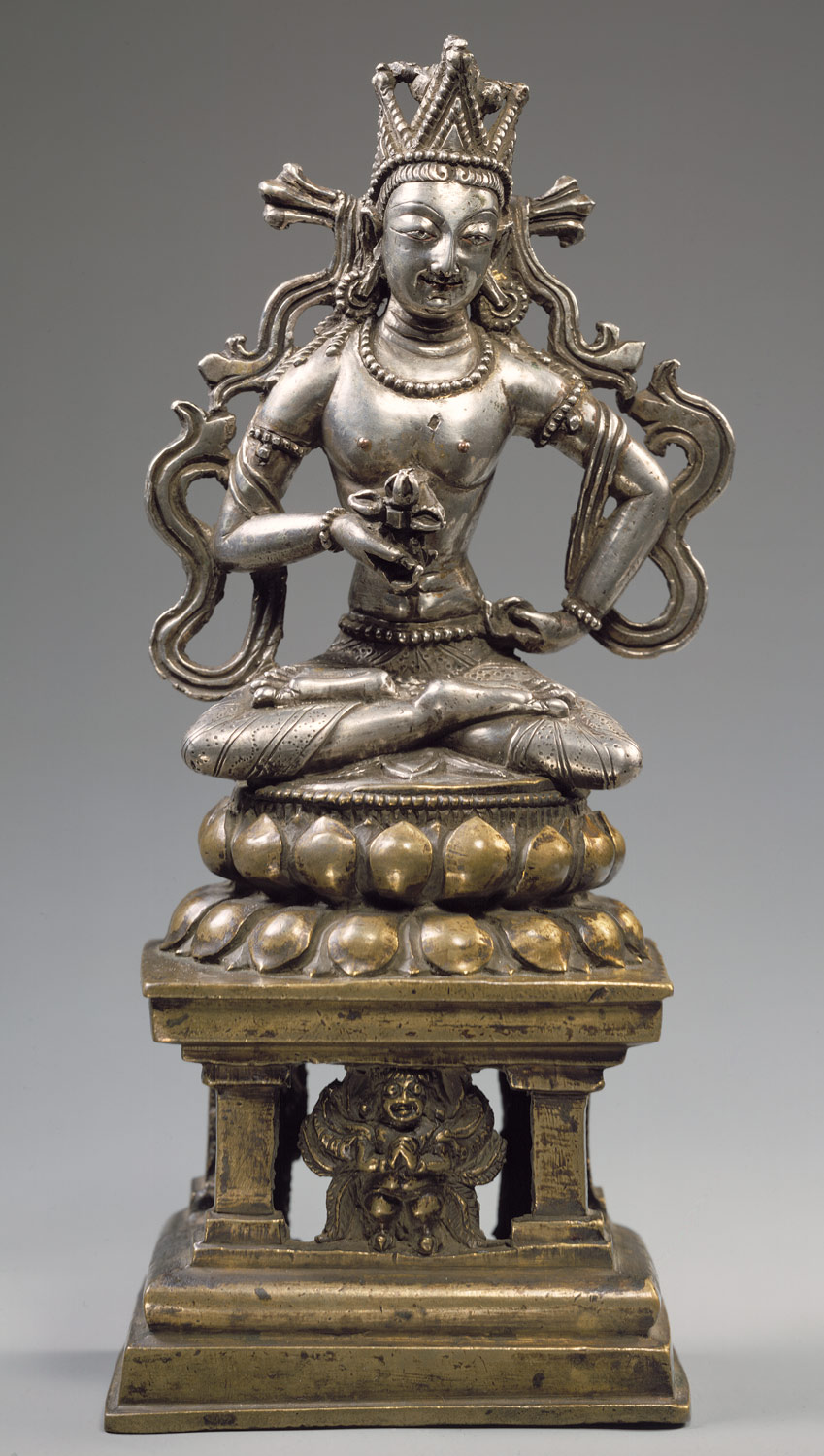
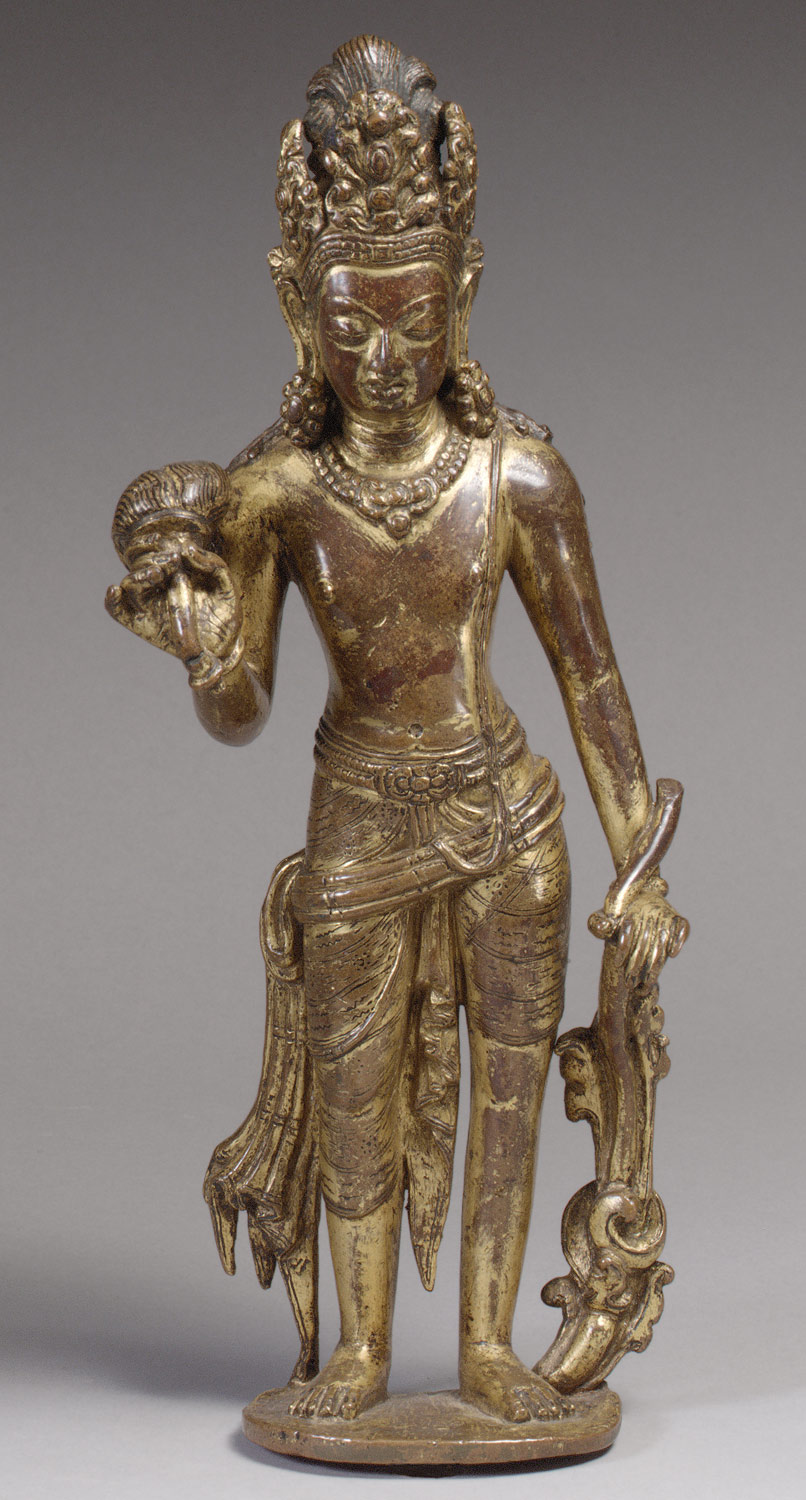
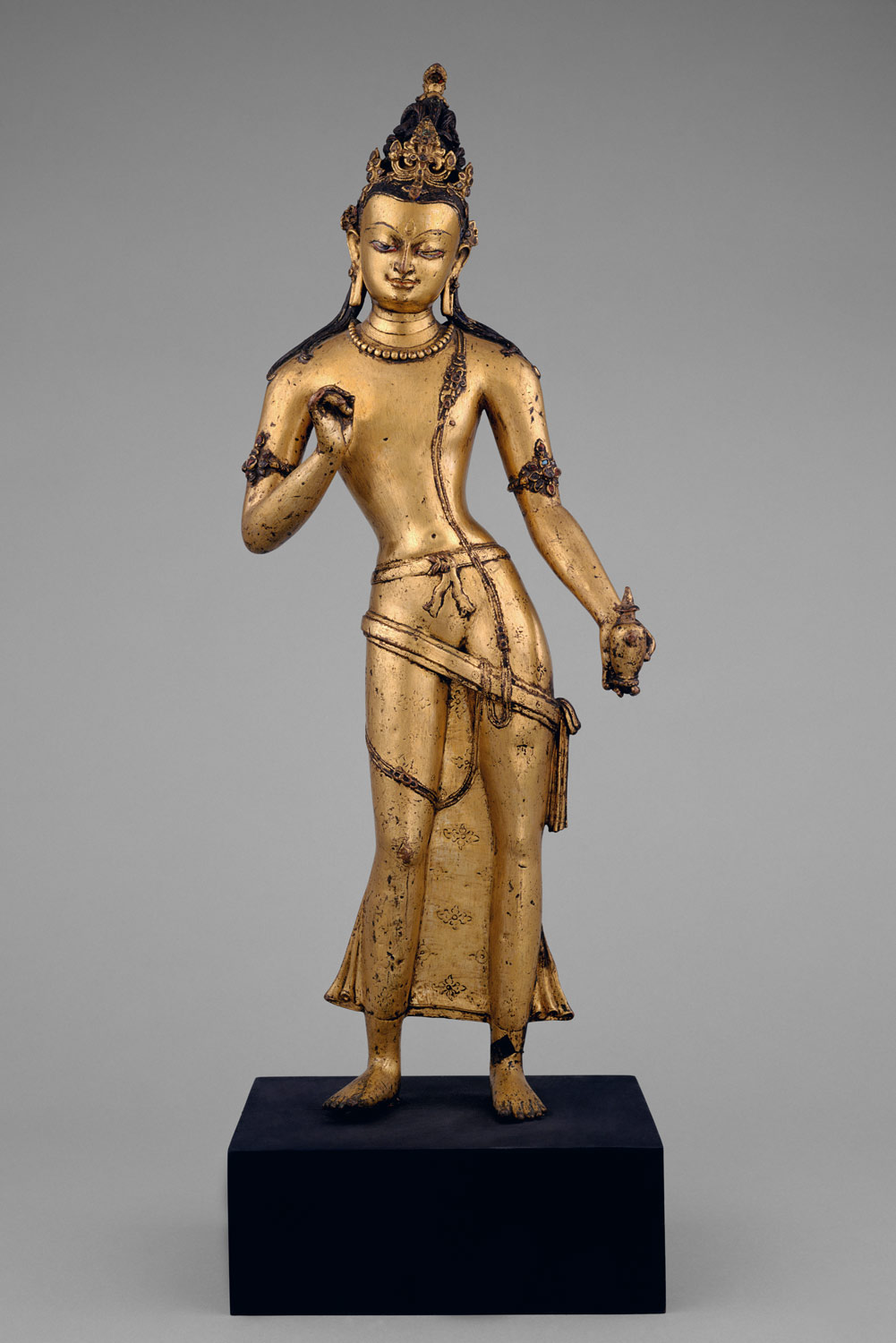
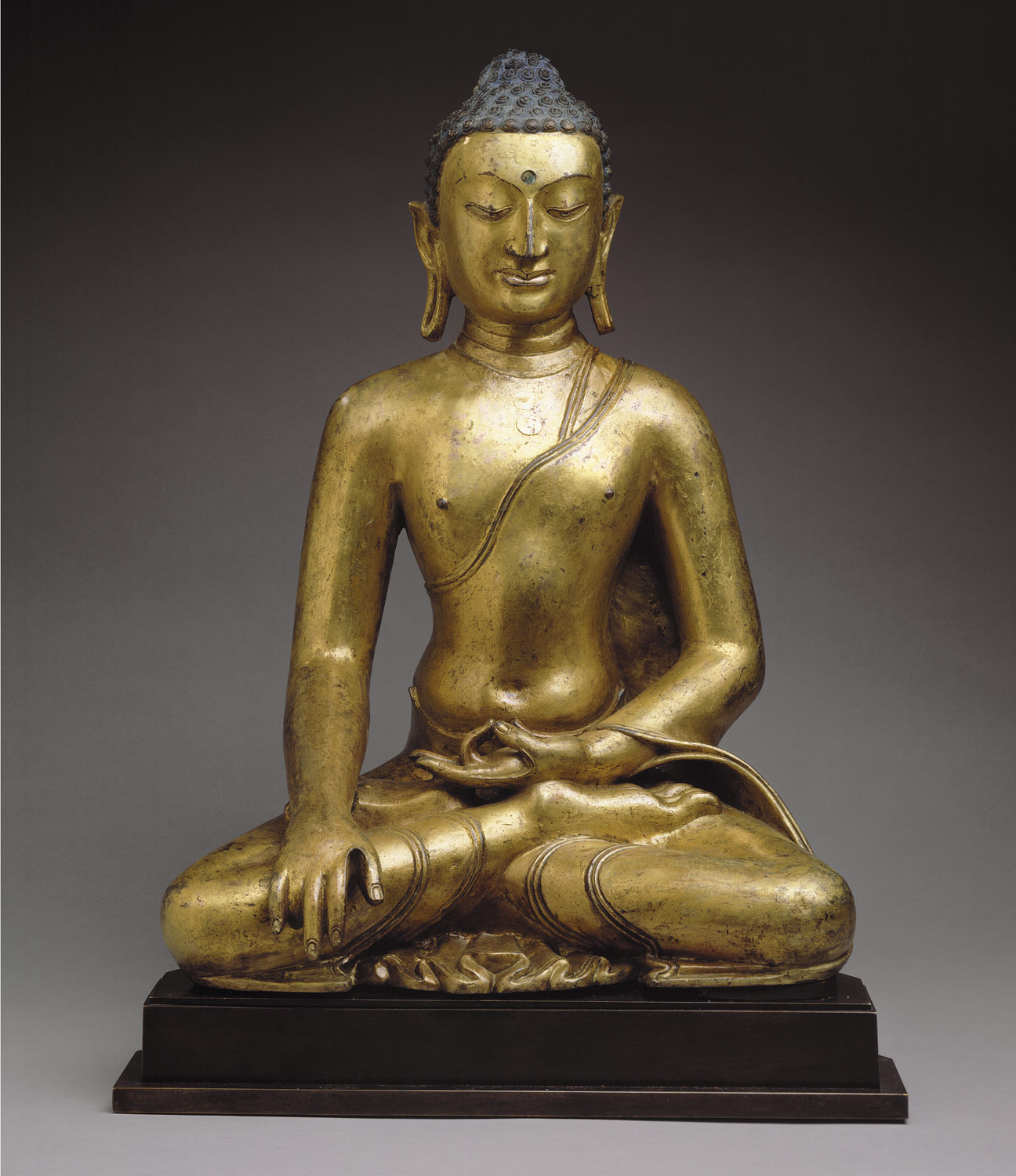
Hinduism and Buddhism fundamentally shape the cultures of the Himalayas, integrating indigenous elements with those imported directly from India. This period is characterized by the active patronage of Buddhism in Tibet under Khri-srong-Ide-btsan (r. ca. 750–97) and contact of Tibetan artists with Buddhist painting traditions in Central Asia (including Khotan and Dunhuang). Buddhism is firmly established in the mid-ninth century in what is now Bhutan, under Tibetan influence. During the ninth century, Buddhism is persecuted in Tibet, but flourishes under state patronage from the eleventh century. Nepal is ruled by the Licchavi family, heralding the profound influence of Indian culture. Hinduism and Buddhism are patronized as Licchavi power wanes around 750, followed by a period of transition about which little is known.
Himalayan Region, 500–1000 A.D.
Timeline
500 A.D.
625 A.D.
NEPAL
625 A.D.
750 A.D.
NEPAL
TIBET
750 A.D.
875 A.D.
NEPAL
TIBET
875 A.D.
1000 A.D.
NEPAL
Overview
Key Events
-
ca. 500 B.C.–600 A.D.
The Monpa, a fierce mountain tribe, are thought by some scholars to inhabit the Lho Mon or Monyul state in the southern lowlands of Bhutan.
-
ca. 400–750
The first Nepali state, ruled by the Licchavi family, marks a golden age of the culture. Close ties are maintained with the Guptas in India, whose aesthetics and literary language are reflected in Nepali art. Buddhism and Hinduism flourish in this period.
-
ca. 570–620
The tribal chief Namri Songzen first attempts to unify Tibet.
-
ca. 600–700
The Kathmandu Valley/Nepal is known as an exporter of fine copper. A Chinese visitor mentions impressive metalwork, but examples are no longer extant.
-
ca. 620–649
Songzen Gampo, Namri Songzen’s son, unifies Tibet under the Yarlung dynasty, beginning a period of expansion into China and Central Asia. He conquers Nepal to the west, Kamarupa to the south, and various tribes along China’s border, and establishes a capital at Lhasa. His marriages to a Nepali princess, fleeing a coup d’etat in 625, and a Tang princess to cement ties to China, seem to have fostered his adoption of Buddhism as a national religion. Songzen Gampo also marries three high-ranking Tibetan women to further consolidate his empire.
-
ca. 630–640
Songzen Gampo orders the construction of two Buddhist temples in Bhutan, introducing Buddhism to the country.
-
ca. 723
The city of Kathmandu is founded.
-
ca. 750–797
Khri-srong-Ide-btsan’s reign is characterized by the active patronage of Buddhism and contact of Tibetan artists with Central Asian painting traditions, particularly at Khotan and Dunhuang.
-
ca. 750–1200
Nepal is ruled by several aristocratic families during the Thakuri or Transitional period.
-
ca. 760–800
Famous Indian mystics such as Santarakshita and Padmasambhava visit Tibet.
-
ca. 763
Tibetan armies seize the Chinese capital at Chang’an. During this period of Tibetan power, Tang China pays tribute to Tibet.
-
ca. 779
The first Buddhist monastery in Tibet is founded at Samye.
-
822
A peace treaty with Tang China marks the high point of the Tibetan empire’s power.
-
ca. 842–850
With the assassination of ruler Langdarma, the Tibetan empire begins to fragment, the royal dynasty collapses, and Buddhism declines.
-
ca. 950
Buddhism begins a resurgence in central Tibet, and Tibetans journey to India and Nepal in search of texts and teachings.
Citation
“Himalayan Region, 500–1000 A.D.” In Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History. New York: The Metropolitan Museum of Art, 2000–. http://www.metmuseum.org/toah/ht/?period=06®ion=ssh (October 2001)
Related
Map