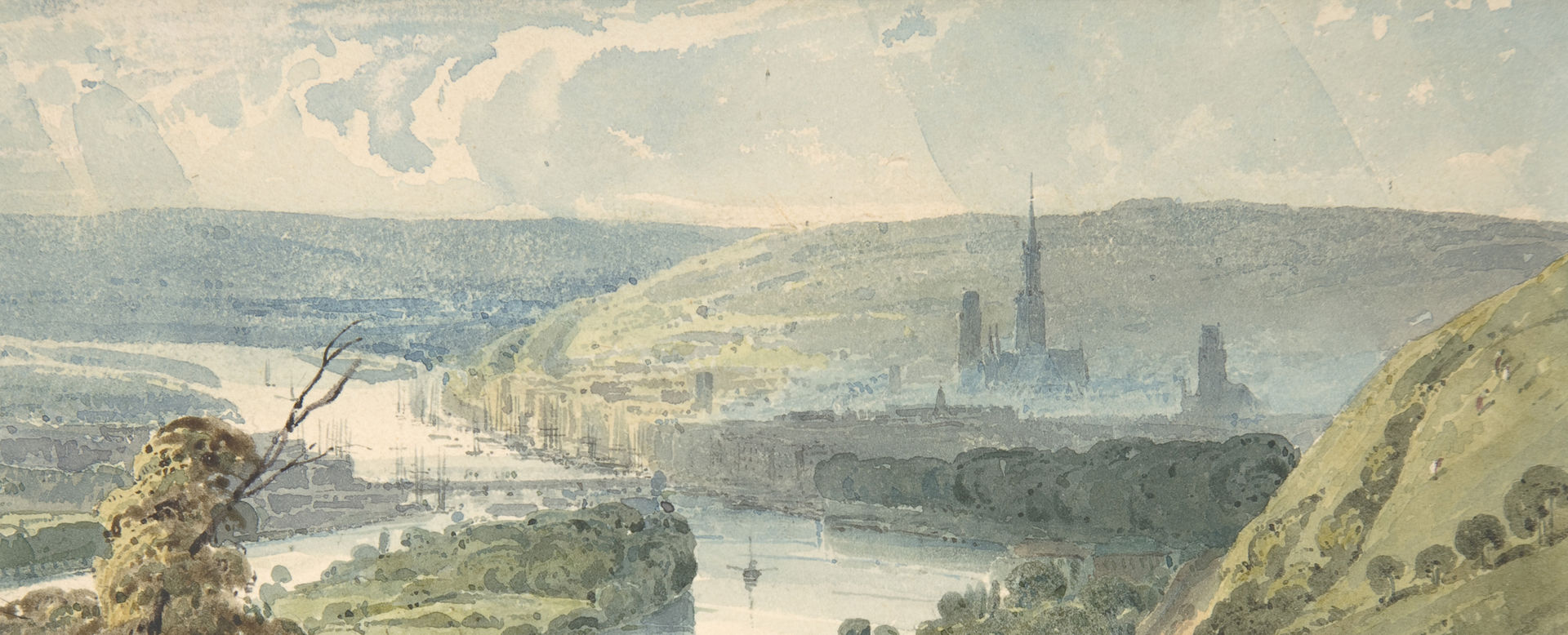The Atlantic Telegraph Cable Fleet Assembled at Berehaven (Southwest Coast of Ireland): Ships, the Great Eastern, H.M.S. Terrible, the Alby, the Medway and the William Cory
Robert Charles Dudley British
Not on view
One of the 19th century's great technological achievements was to lay a telegraphic cable beneath the Atlantic, allowing messages to speed back and forth between North America and Europe in minutes, rather than ten or twelve days by steamer. An initially successful attempt in 1858, led by Cyrus W. Field and financed by the Atlantic Telegraph Company, failed after three weeks. Two working cables were finally laid in July and September 1866, the result of repeated efforts by the indefatigable Field, a cadre of engineers, technicians, and sailors, two groups of financial backers, and significant help from the British and United States navies. Dudley documented the process in a series of watercolors and oils, this example showing the Great Eastern and support vessels anchored in Bantry Bay, before setting out on July 12, 1866. On July 28 the fleet reached Trinity Bay, having laid 1,960 miles of working cable. Once spliced to the shore cable at Heart's Content, Newfoundland, a working cross-Atlantic connection was established, prompting international rejoicing. In 1892 Field donated art works by Dudley, commemorative medals, memorabilia, and specimens of cable to the Museum.
This image cannot be enlarged, viewed at full screen, or downloaded.